A:计算平均绩点 思路分析 由题意得,要计算平均学分绩点只需要计算总的课程学分绩点和总课程学分即可,我们用数组$a$,$b$来存储有效数据,$a[i]$记录第$i$门课程的学分,$b[i]$记录第i门课程的成绩。$score$存学分总数,$ans$存学分绩点。最后输出$ans$和$score$的比值。注意在多组数据输入中,重复使用的$score$和$ans$要记得在循环中置零。
c代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include "stdio.h" int main () { int t,n; double a[110 ],b[110 ]; scanf ("%d" ,&t); while (t--) { double score = 0 ; scanf ("%d" ,&n); for (int i=0 ; i<n; i++) { scanf ("%lf" , &a[i]); score += a[i]; } for (int i=0 ; i<n; i++) scanf ("%lf" ,&b[i]); double ans = 0 ; for (int i=0 ; i<n; i++) if (b[i] >= 60 ) ans += (b[i] - 50 ) / 10 * a[i]; printf ("%.2lf\n" ,ans/score); } return 0 ; }
B:矩阵对换 思路分析
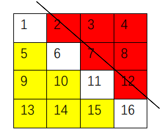
如上图在对称线右上方的红色元素满足:$i<=j-k$,其中$i$为行号$j$为列号$k$为对称线向上平移的单位长度。
c/c++代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 #include <stdio.h> int a[110 ][110 ], n, k;void swap (int * a, int * b) { int t = *a; *a = *b; *b = t; } int main () { scanf ("%d%d" , &n, &k); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++ ) for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j ++ ) scanf ("%d" , &a[i][j]); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++ ) for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j ++ ) if (i <= j - k) swap(&a[i][j], &a[j][i]); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++ ) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j ++ ) printf ("%d " , a[i][j]); puts ("" ); } return 0 ; }
C:二进制小发现 思路分析 这道题目是一个二进制题.
c/c++代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () string a; cin >> a; long long ans = 0 ,r = a.size (); while (r != 1 ){ ans ++; if (a[r - 1 ] == '0' ){ r --; }else { for (int i = r - 1 ;i >= 0 ;i --){ if (a[i] - '0' + 1 > 1 ){ a[i] = '0' ; }else { a[i] = '1' ; break ; } } } } if (a[0 ] == '0' ){ cout << ans + 1 << endl; }else { cout << ans << endl; } }
D:三重 思路分析 这个题目意思很简单,就是输出所有出现次数超过3次的数,我们利用一个table数组存储每个数字出现的次数,输入结束后遍历一遍table数组进行判断输出即可。
c代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #include "stdio.h" int main () { int t,n; int x,table[200010 ]; scanf ("%d" ,&t); while (t--){ int flag = 1 ; scanf ("%d" ,&n); for (int i=0 ; i<n; i++) { scanf ("%d" , &x); table[x]++; } for (int i=0 ; i<=n; i++) if (table[i] >= 3 ) { printf ("%d " ,i); flag = 0 ; } if (flag) printf ("-1\n" ); else puts ("" ); for (int i=0 ; i<=n; i++) table[i] = 0 ; } return 0 ; }
E:找出01数 解法一:二进制枚举 思路分析
分析题目可以知道每一位要么是$0$要么是$1$,$n$最大是 $10^9$,所以最多有$10$位,而实际上在填的时候只有$9$位数字,
c/c++代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #include <stdio.h> int main () { int n; scanf ("%d" , &n); int res = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < (1 << 10 ); i ++ ) { int x = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < 10 ; j ++ ) { x = x * 10 + (i >> j & 1 ); } if (x <= n){ res ++; } } printf ("%d" , res); return 0 ; }
python代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution : def process (self ): n = int (input ()) res = 0 for i in range (1 , 1 << 10 ): x = 0 for j in range (10 ): x = x * 10 + (i >> j & 1 ) if x <= n: res += 1 return res if __name__ == '__main__' : print (Solution().process())
java代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import java.util .Scanner ;class Main { int solve ( Scanner sc = new Scanner (System .in ); int n = sc.nextInt (), res = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < (1 << 10 ); i ++ ) { int x = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < 10 ; j ++ ) { x = x * 10 + (i >> j & 1 ); } if (x <= n){ res ++; } } return res; } public static void main (String [] args Main main = new Main (); System .out .println (main.solve ()); } }
解法二:DFS 思路分析
代码很简洁看了就懂了。
c/c++代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #include <iostream> using namespace std;int res, n;void dfs (int u) if (u > n) return ; dfs (u * 10 ); dfs (u * 10 + 1 ); res ++; } int main () cin >> n; dfs (1 ); cout << res << endl; return 0 ; }
F:元素加一 思路分析
这个题目经分析可得,为了让所有的元素彼此相等,我们只能选择元素加一,所以最后变成的数一定是最大的那个数,因为它不能变小,只能通过让其他的小于它的数变大和它相等。最多进行的操作就是从最小的数变成最大的数,在 min < x < max max - min 的值.
c代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 #include "stdio.h" int main () { int a; int t,n; scanf ("%d" ,&t); while (t--){ int max = 0 , min = 1e9 ; scanf ("%d" ,&n); for (int i=0 ; i<n; i++){ scanf ("%d" ,&a); if (a > max) max = a; if (a < min) min = a; } printf ("%d\n" ,max - min); } return 0 ; }
G:词排列 思路分析
这道题目就是一道分析题
再根据词 649 和词 650 以及词 27 可以发现如果第二个字符小于第一个字符时它的索引就是
c/c++代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int t; cin >> t; while (t --){ string a; cin >> a; int sum = 0 ; if (a[1 ] - 'a' < a[0 ] - 'a' ){ sum += (a[0 ] - 'a' ) * 25 + (a[1 ] - 'a' ) + 1 ; }else { sum += (a[0 ] - 'a' ) * 26 + (a[1 ] - a[0 ]); } cout << sum << endl; } }
H: 奇数/偶数增量 思路分析 通过题目我们可以知道,我们只能对奇索引单独操作或者对偶索引单独操作,这样的话我们就得到一个信息:
如果奇索引的元素中存在一个和其他奇索引的奇偶性不同,则这个数组里的元素不能全部变为偶数或奇数
同理,如果偶索引的元素中存在一个和其他偶索引的奇偶性不同,则为 “NO”
例:有一个长度为四的数组 a ,a[0] = 1,a[1] = 1,a[2] = 2,a[3] = 2,因为 a[1] 与 a[3]的奇偶性不同,这个数组不能全部变为偶数或奇数;同理 a[0] 与 a[2] 奇偶性也不同
c/c++代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 51 ;int a[N],even[N],odd[N];int main () int t; cin >> t; while (t --){ int n; cin >> n; int p = 0 ,p1 = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ;i <= n;i ++){ cin >> a[i]; if (i % 2 == 0 ){ even[p] = a[i]; p ++; }else { odd[p1] = a[i]; p1 ++; } } int sum = 0 ,sum1 = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ;i < p;i ++){ if (even[i] % 2 == 0 ){ sum ++; } } for (int i = 0 ;i < p1;i ++){ if (odd[i] % 2 == 0 ){ sum1 ++; } } if ((sum == p || sum == 0 ) && (sum1 == p1 || sum1 == 0 )){ cout << "YES" << endl; }else { cout << "NO" << endl; } } return 0 ; }
I:奖学金评定 思路分析
这个题目只需要根据输入的n来进入分支结构即可。
c代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #include "stdio.h" int main () { int t; double n; scanf ("%d" ,&t); while (t--){ scanf ("%lf" ,&n); if (n >= 4.0 ) puts ("special scholarship" ); else if (n >= 3.5 ) puts ("first-class scholarship" ); else if (n >= 3.0 ) puts ("second-class scholarship" ); else if (n >= 2.5 ) puts ("third-class scholarship" ); else puts ("none" ); } return 0 ; }
J:数字转换 思路分析 这是一个思维题,当你看到题目输出格式上加粗的字时,
c代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include "stdio.h" int main () { int x,y,a,b; int t; scanf ("%d" ,&t); while (t--) { scanf ("%d %d" ,&x,&y); if (y % x == 0 ) printf ("%d %d\n" ,1 ,y/x); else printf ("0 0\n" ); } return 0 ; }
K: 无限替换 思路分析 对于题目的分析我们可以得到三点信息
t 串中含有 a 字符时而且 t 串长度大于一,替换的时候一直循环下去得到的答案是无限大的.
t 串中含有 a 字符时而且 t 串长度等于一,替换的时候只有一种结果也就是其本身.
t 串中不含 a 字符,替换之后得到不同的串的数量只能是 2 的 t.size() 次方.
c/c++代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int t; cin >> t; while (t --){ string a,b; cin >> a >> b; bool flag = false ; for (int i = 0 ;i < b.size ();i ++){ if (b[i] == 'a' ){ flag = true ; } } if (flag && b.size () > 1 ){ cout << "-1" << endl; }else if (flag && b.size () == 1 ){ cout << "1" << endl; }else if (!flag){ cout << (long long )pow (2 ,a.size ()) << endl; } } }